Author: Devika R
October 20, 2025
6 min read
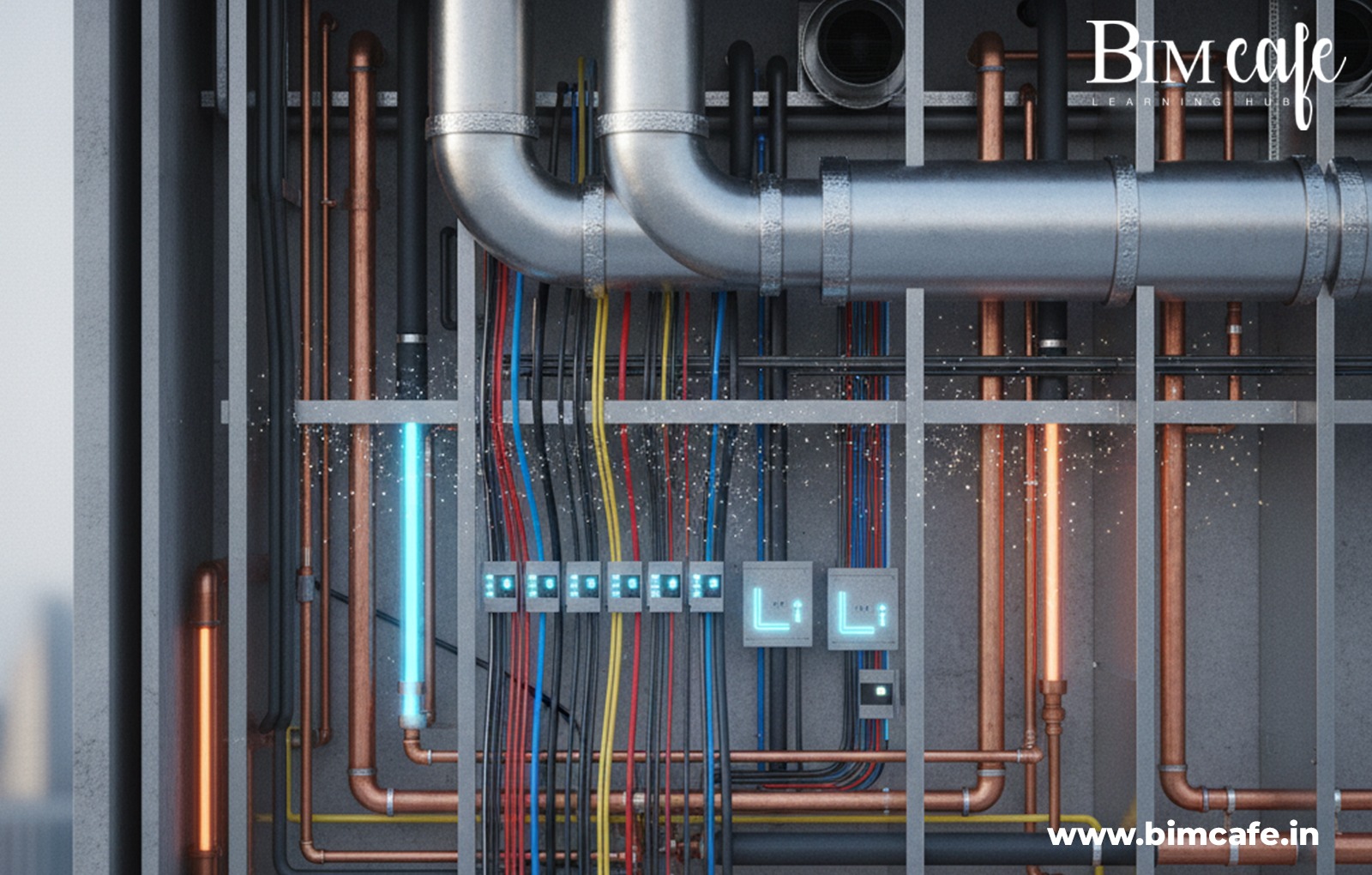
Every building tells a story — of design, safety, comfort, and function. But behind its shining façade lies an invisible network of systems that make it all work: the air we breathe, the light we use, and the water we rely on every day. These lifelines are governed by something most people never see or think about — MEP codes.
MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) codes form the backbone of safe and efficient building design. They ensure that every pipe, wire, and duct is installed the right way, meeting standards for safety, performance, and sustainability.
In today’s construction world — especially with the rise of BIM (Building Information Modeling) — understanding and following these codes isn’t just a formality; it’s a foundation for success. This blog explores why MEP codes matter, how they shape modern projects, and why code-compliant professionals are in such high demand across India’s construction industry.
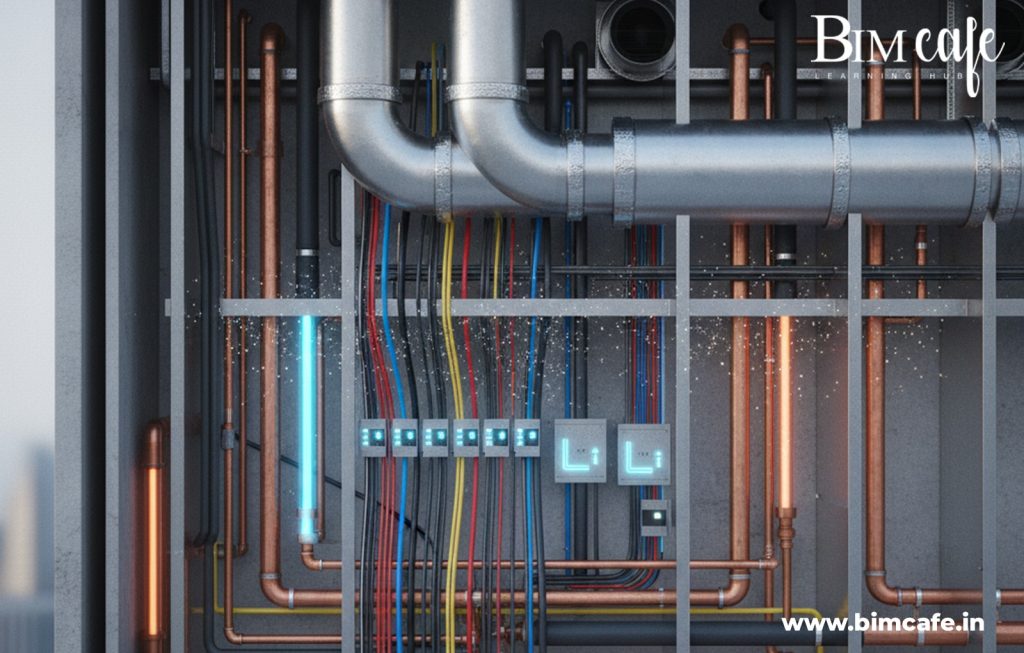
What Are MEP Codes?
MEP codes are comprehensive standards that govern the design, installation, and maintenance of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems within buildings. Their primary goal is to ensure that all building services operate safely, efficiently, and sustainably, protecting both occupants and infrastructure. By adhering to these codes, construction projects achieve higher quality, reduced risk, and better long-term performance.
MEP codes cover several key areas:
- Mechanical Systems (HVAC & Ventilation):
These codes regulate heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning design. They define standards for airflow, ductwork, insulation, indoor air quality, thermal comfort, noise control, and fire-rated ducts, ensuring safe and efficient operation. Modern mechanical codes also account for IoT sensors and smart HVAC systems, which monitor performance in real time. - Electrical Systems:
Electrical codes govern power distribution, lighting, grounding, circuit protection, emergency power, and renewable energy integration. They prevent hazards such as overloads, short circuits, and electrical fires. Compliance ensures energy-efficient systems, reliable operations, and safe integration of advanced technologies like solar panels or battery backups. - Plumbing Systems:
Plumbing codes cover water supply, drainage, venting, sanitation, gas piping, and rainwater management. They ensure clean water, prevent contamination, and regulate pressure systems. Compliance with plumbing codes also promotes water conservation, an essential factor in sustainable urban development. - Fire and Life Safety Systems:
These codes define requirements for sprinklers, fire alarms, smoke detectors, hydrants, and evacuation pathways. They coordinate with mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems to prevent and control fire hazards, ensuring safe evacuation while preserving building functionality and aesthetics.
In India, MEP designs typically align with the National Building Code (NBC), the Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC), and various local fire and electrical regulations, ensuring both legal compliance and global best practices.
Why MEP Codes Are the Silent Heroes of Every Building
MEP codes may be invisible, but their impact is profound. They touch every aspect of a building’s safety, performance, and operational efficiency.
1. They Keep People Safe
The most critical role of MEP codes is life safety:
- Proper electrical wiring prevents fires caused by overloads or short circuits.
- Adequate ventilation maintains healthy indoor air quality, reducing respiratory hazards.
- Fire suppression systems such as sprinklers and alarms contain fires before they escalate.
Without adherence to MEP codes, even a minor installation error can lead to catastrophic failures, making the building a potential hazard for occupants and property.
2. They Ensure Comfort and Functionality
Beyond safety, MEP codes guarantee that buildings are functional and comfortable for occupants:
- Reliable power ensures uninterrupted electricity for lighting, appliances, and critical systems.
- HVAC systems maintain consistent indoor temperatures and air quality, essential for offices, hospitals, and hospitality spaces.
- Safe plumbing ensures a continuous supply of clean water and proper sanitation.
Imagine a hotel or office with flickering lights, poor air circulation, or inconsistent water supply — such failures directly impact user experience and operational efficiency. MEP codes prevent these issues by setting performance standards for every system.
3. They Improve Energy Efficiency
Modern MEP codes incorporate principles of sustainable design and energy conservation:
- High-efficiency HVAC systems reduce energy consumption.
- LED lighting standards minimize electricity use while providing adequate illumination.
- Water-saving fixtures conserve water without compromising performance.
For developers and facility owners, compliance translates into long-term operational savings, reduced carbon footprint, and enhanced sustainability ratings.
4. They Simplify Government Approvals
Local authorities strictly enforce MEP codes during the permitting process. Non-compliant designs can result in:
- Project delays due to inspection failures
- Costly redesigns or modifications
- Temporary halts or shutdowns
Adhering to codes from the design stage ensures smoother approvals, faster project execution, and reduced risk of penalties.
5. They Build Trust and Reputation
Compliance with MEP codes signals professionalism and reliability in the competitive AEC industry:
- Contractors and engineers who follow codes are viewed as credible and competent.
- Clients and collaborators trust code-compliant professionals for high-value projects and global partnerships.
- Firms that prioritize MEP compliance demonstrate a commitment to safety, quality, and sustainability, enhancing their market reputation.
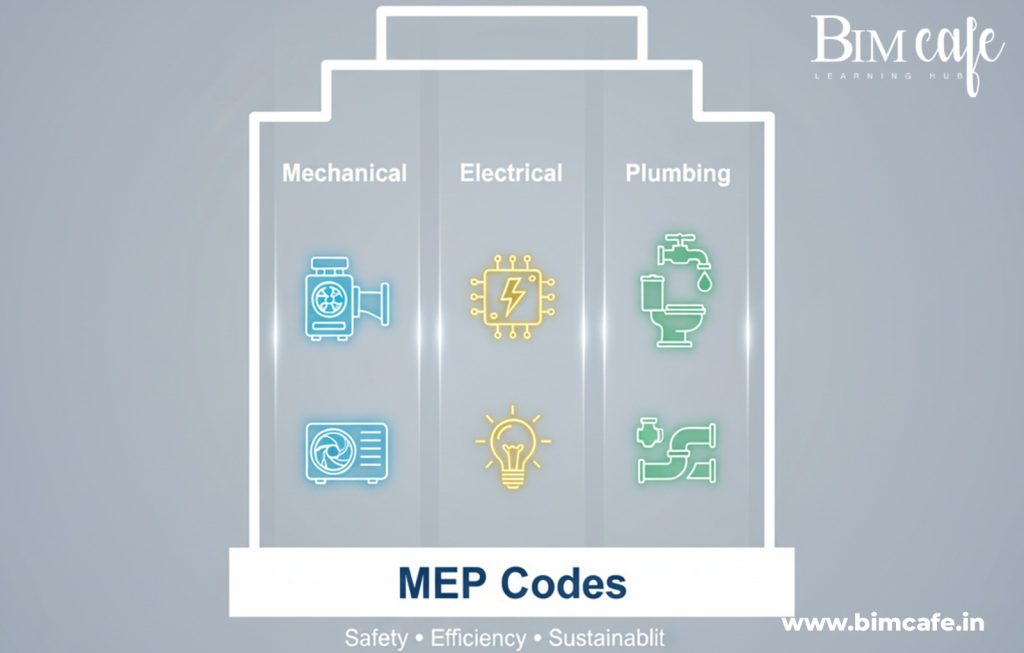
Key Areas Covered by MEP Codes
MEP codes are essential for ensuring that all building systems operate safely, efficiently, and sustainably. Each discipline — mechanical, electrical, plumbing, and fire/life safety — has specific standards that guide design, installation, and maintenance. Let’s explore each in detail.
Mechanical Codes (HVAC and Ventilation)
Mechanical codes govern all aspects of heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) systems. Their primary goal is to maintain indoor air quality (IAQ), thermal comfort, and energy efficiency.
Key requirements include:
- Airflow and Air Changes: Specifies minimum ventilation rates to maintain healthy indoor environments.
- Duct Materials and Insulation: Defines acceptable materials, insulation standards, and durability requirements to optimize energy use.
- Noise and Vibration Control: Limits noise from HVAC systems to prevent discomfort in occupied spaces.
- Fire Safety: Mandates fire-rated ducts and smoke extraction systems in case of emergencies.
- Energy Performance: Ensures HVAC designs meet efficiency and sustainability standards.
Modern mechanical design often incorporates smart sensors and IoT-based monitoring, allowing real-time performance tracking while remaining compliant with mechanical codes. This integration helps reduce energy consumption, predict maintenance needs, and improve occupant comfort.
Electrical Codes
Electrical codes define standards for power distribution, safety, and energy efficiency in buildings. They ensure that electrical systems are reliable and hazard-free.
Key components include:
- Wiring Layout and Grounding: Ensures safe installation of circuits and prevents electrical hazards.
- Circuit Protection: Specifies fuses, breakers, and overload protection to prevent short circuits and fires.
- Voltage and Load Limits: Regulates maximum voltage drops and system loads for safe operation.
- Integration of Renewable Energy: Defines standards for safely connecting solar panels, batteries, and other renewable systems.
- Emergency Systems: Covers fire alarms, egress lighting, and backup power systems.
A well-designed electrical system reduces downtime, enhances energy efficiency, and minimizes risk, ensuring uninterrupted operation of all critical building functions.
Plumbing Codes
Plumbing codes govern water supply, drainage, sanitation, and gas systems, ensuring public health and efficient water management.
Key provisions include:
- Water Supply and Pressure Systems: Ensures safe and adequate water flow throughout the building.
- Backflow Prevention: Prevents contamination of potable water through non-compliant connections.
- Sanitary and Rainwater Systems: Regulates installation of sewage, drainage, and rainwater harvesting systems.
- Water Conservation: Encourages low-flow fixtures and greywater recycling for sustainable usage.
With urban India embracing sustainable water management, plumbing codes have become increasingly important, helping reduce wastage, prevent contamination, and promote eco-friendly practices.
Fire and Life-Safety Codes
Fire and life-safety codes are critical for protecting occupants and property during emergencies. They integrate with all other MEP systems to provide comprehensive safety coverage.
Key elements include:
- Sprinklers, Hydrants, and Alarms: Mandates installation of fire suppression and detection systems throughout the building.
- Evacuation Systems: Specifies placement of fire exits, signage, and emergency escape routes.
- Coordination with MEP Systems: Ensures smoke control, ventilation, and fire suppression systems operate seamlessly during emergencies.
- Architectural Integration: Codes ensure safety measures do not compromise building aesthetics or functionality.
Integrating fire safety early in design minimizes risks while allowing efficient building layouts and occupant protection.
MEP Codes and BIM: The Perfect Partnership
The advent of Building Information Modeling (BIM) has transformed how MEP codes are applied, making compliance more efficient, accurate, and collaborative. Using tools like Revit, Navisworks, and BIM 360, engineers can simulate and validate MEP designs before any physical installation, reducing risk and rework.
BIM enables:
- Automated Rule-Based Checks: Systems can verify clearances, dimensions, and compliance with code standards automatically.
- Clash Detection: Identifies conflicts between mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems to prevent costly onsite errors.
- Energy Simulation: Verifies HVAC, electrical, and plumbing performance against efficiency standards.
- Integrated Documentation: Generates submission-ready reports for authority approvals and audits.
This “code-aware design” approach enhances collaboration between architects, engineers, and contractors, ensures compliance, and saves time and cost while improving project quality.
How Non-Compliance Affects Projects
Failure to adhere to MEP codes can have serious consequences, impacting safety, finances, timelines, and reputation. Understanding these risks highlights why compliance is not just a regulatory requirement but a critical part of project success.
1. Delays During Inspections or Permit Approvals
MEP code violations are a common reason for inspection failures. Authorities may reject designs or installations that don’t meet required standards, leading to:
- Extended project timelines due to repeated inspections.
- Delays in securing necessary permits for construction or occupancy.
- Postponed handover of the building, affecting stakeholders and clients.
Early integration of MEP code compliance in the design phase helps avoid these costly delays.
2. Cost Overruns from Redesign or Rework
Non-compliant systems often require expensive modifications or complete redesigns:
- Incorrect duct layouts or wiring may need demolition and reinstallation.
- Plumbing misconfigurations can require extensive corrective work.
- Fire and life-safety violations can halt construction until rectified.
Such rework increases labor, material, and operational costs, sometimes exceeding the original budget.
3. Safety Hazards
Ignoring MEP codes puts both occupants and property at significant risk:
- Electrical faults may trigger fires or shocks.
- Inadequate ventilation can lead to poor indoor air quality and health issues.
- Faulty plumbing or drainage systems may cause water damage or contamination.
- Insufficient fire safety measures increase vulnerability during emergencies.
Compliance ensures that all systems function safely, reliably, and predictably, protecting lives and assets.
4. Legal Liabilities and Penalties
Non-compliance can expose project owners, engineers, and contractors to legal risks:
- Fines and penalties from regulatory authorities.
- Liability claims in case of accidents or system failures.
- Potential lawsuits for negligence or non-conformance with building codes.
Adhering to MEP codes mitigates these risks and provides legal protection.
5. Reputation Loss in a Regulated Industry
In the competitive AEC (Architecture, Engineering, Construction) sector, reputation is paramount:
- Clients and partners expect code-compliant projects.
- Repeated violations can damage credibility and hinder future business opportunities.
- Non-compliance reflects poorly on the professionalism of engineers, contractors, and project teams.
By following MEP codes, companies demonstrate reliability, technical competence, and commitment to safety, building trust with clients and stakeholders.

Emerging Trends in MEP Code Integration
The construction industry is evolving rapidly, and MEP codes are keeping pace with technological advances, sustainability demands, and digital workflows. Modern trends are reshaping how engineers, architects, and contractors ensure compliance:
1. Smart and Automated Code Checking
AI-powered software now allows engineers to review digital drawings automatically, flagging non-compliant elements without manual intervention. These tools reduce review time, improve accuracy, and minimize human error, enabling faster design approvals and higher-quality outcomes.
2. Sustainable Design and Energy Codes
Environmental consciousness has made sustainability a central focus of MEP codes. Modern regulations emphasize:
- Integration of renewable energy sources such as solar panels and heat pumps.
- Carbon-neutral HVAC systems for reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Low-water plumbing fixtures and greywater recycling systems to conserve resources.
These requirements ensure buildings not only operate efficiently but also contribute to global sustainability goals.
3. Prefabricated MEP Modules
Prefabrication is transforming site efficiency. Factory-built, pre-tested MEP modules ensure each component complies with relevant codes before installation. Benefits include:
- Reduced onsite labor and errors
- Faster project timelines
- Higher quality and standardization
By adopting modular MEP systems, projects maintain consistent compliance while minimizing delays and costs.
4. Digital Twin Integration
Post-construction, digital twins allow building operators to monitor systems in real time, track performance, and ensure ongoing code compliance. Sensors feed live data into BIM platforms, enabling predictive maintenance and operational optimization. This integration transforms buildings into smart, self-monitoring structures.
5. Skill Development and Training
With evolving technologies and stricter regulations, skilled professionals are in high demand. Organizations like BIM Cafe Learning Hub train engineers, architects, and BIM professionals to:
- Apply MEP codes effectively using BIM workflows
- Conduct clash detection, energy simulation, and code verification
- Prepare projects for global compliance standards
This training ensures professionals are job-ready and industry-aligned, bridging the gap between education and high-value employment opportunities.
Best Practices for MEP Code Compliance
Ensuring compliance requires a proactive, structured approach throughout the project lifecycle:
- Start Early: Integrate code requirements from the concept stage to prevent costly redesigns.
- Coordinate Frequently: Conduct interdisciplinary reviews between architectural, structural, and MEP teams to catch conflicts early.
- Use Digital Tools: Leverage BIM platforms for real-time validation, automated checks, and clash detection.
- Document Everything: Maintain detailed records of design decisions, inspections, and approvals for audits.
- Stay Updated: MEP codes evolve continuously; professionals should undergo refresher training and monitor regulatory changes.
- Engage Authorities Early: Clarify local interpretations of codes to avoid confusion and project delays.
Following these best practices ensures smooth approvals, safe and efficient systems, and predictable project outcomes.
Why MEP Code Knowledge Is a Career Booster
Proficiency in MEP codes and BIM integration significantly enhances career prospects for engineers, architects, and construction professionals:
- Countries like the UAE, UK, and Singapore strictly enforce MEP and BIM standards, creating high demand for skilled professionals.
- Knowledge of code-compliant BIM workflows ensures eligibility for global projects and positions professionals for leadership roles.
- Training on real-world BIM projects aligned with MEP codes, such as those offered at BIM Cafe Learning Hub, equips professionals with practical skills and placement assurance in leading AEC firms.
In essence, mastering MEP codes is not just about compliance — it’s a gateway to higher employability, international opportunities, and professional credibility.
Conclusion
MEP codes form the invisible backbone of every building, ensuring that mechanical, electrical, and plumbing systems operate safely, efficiently, and sustainably throughout the building’s lifecycle. Compliance is no longer just a regulatory formality; it is a critical enabler of quality, reliability, and long-term performance.
As the construction industry embraces smart design, BIM integration, and digital twins, understanding and applying MEP codes has become a key professional skill. Engineers, architects, BIM specialists, and construction managers who are proficient in these codes can:
- Design systems that meet global standards and regulatory requirements.
- Reduce errors, rework, and safety hazards during construction.
- Ensure efficient operations, energy savings, and sustainable building performance.
- Enhance professional credibility and unlock high-value career opportunities worldwide.
Whether you are a student, a practicing architect, or a construction manager, mastering MEP codes equips you to create safer, smarter, and more sustainable spaces — buildings that are future-ready and aligned with the evolving demands of 2025 and beyond.