Author: Devika R
February 18, 2026
9 min read
The Architecture, Engineering, and Construction industry is rapidly evolving toward connected, data-driven delivery models. Cloud-Based BIM has become a major driver of this change, allowing distributed teams to collaborate in real time while maintaining a reliable single source of project information.
Instead of exchanging static files, professionals now work within shared digital ecosystems. Models, drawings, schedules, and documentation stay synchronized across disciplines. The outcome is better coordination, improved transparency, and faster decision-making.
As project scale and stakeholder expectations grow, cloud-enabled BIM workflows are moving from innovation to necessity.
What Is Cloud-Based BIM?
Cloud-Based BIM refers to the practice of storing, managing, and collaborating on Building Information Models through secure online platforms instead of isolated desktops, local servers, or email-based file exchanges.
Rather than moving drawings from person to person, teams connect to a centralized digital environment where information remains live, structured, and continuously updated.
In a cloud-enabled workflow:
- The model becomes a shared resource, not an individual file
- Every stakeholder views the same version of truth
- Data flows across disciplines without manual redistribution
- Project history is recorded automatically
Authorized users can:
- Access information from offices, homes, or construction sites
- Contribute to models at the same time
- Review updates as they happen
- Track revisions and ownership
- Follow formal approval pathways
- Retrieve previous versions when needed
Because the system is centralized, conflicts caused by outdated files, duplicate drawings, or miscommunication are drastically reduced.
This method is essential for Integrated Project Delivery (IPD), where architects, engineers, contractors, and owners must operate within a coordinated digital framework.
In simple terms:
👉 Instead of sending files, teams share environments.
Why the AEC Industry Is Shifting Toward Cloud Workflows
Modern construction is more complex than ever.
Projects now involve:
- Larger consultant networks
- Global design participation
- Shorter delivery timelines
- Higher quality expectations
- Strict regulatory compliance
Traditional workflows based on emailing drawings or uploading static files cannot keep pace with these demands.
They often lead to:
- Version confusion
- Lost communication trails
- Delayed approvals
- Repetitive rework
- Reduced trust in information
Cloud-based systems address these problems by creating a continuous, traceable data environment.
They enable:
- Unified access to current project information
- Elimination of parallel file versions
- Instant communication between stakeholders
- Transparent responsibility tracking
- Faster review cycles
- Improved forecasting and risk management
The growth of remote collaboration has further strengthened this transition. Teams no longer need physical proximity to participate effectively in design and coordination.
For international firms, cloud workflows make cross-border collaboration practical and efficient.
The Foundation: Common Data Environment (CDE)
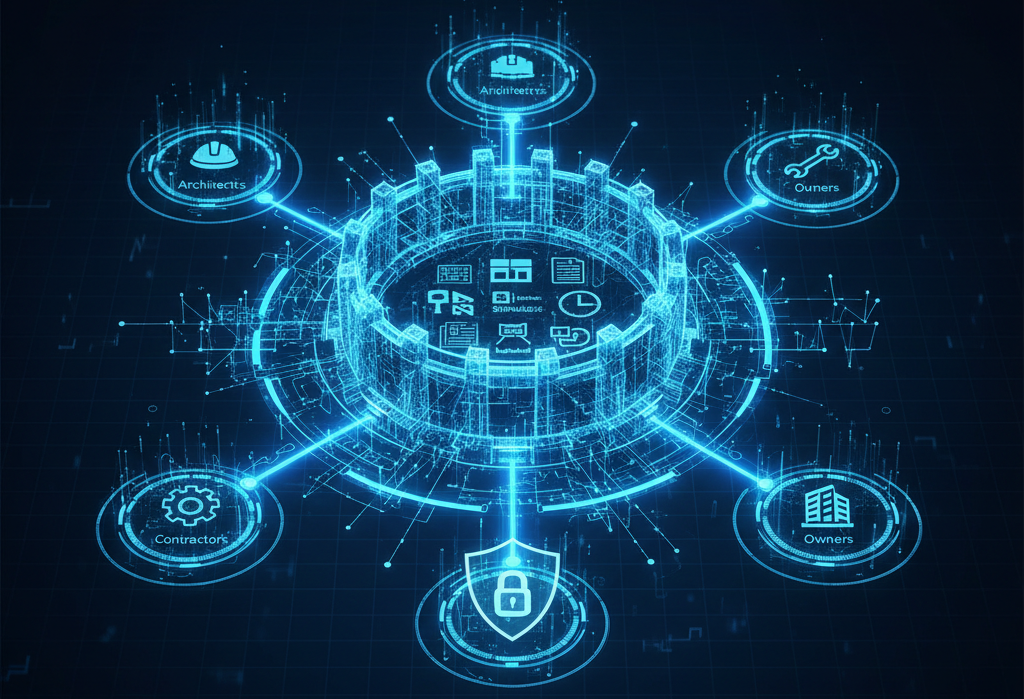

A Common Data Environment is the operational heart of cloud collaboration.
It is not just storage.
It is a structured system that controls how information is created, reviewed, approved, and shared throughout the project lifecycle.
Within a well-managed CDE, teams can:
- Store discipline models in organized folders
- Maintain drawing registers
- Issue and receive transmittals
- Control revision numbering
- Apply approval workflows
- Restrict access based on user roles
- Preserve audit trails
- Archive finalized information
Because every action is recorded, accountability becomes measurable and defensible.
Most modern CDE implementations align with international standards such as ISO 19650, which define best practices for information management in BIM projects.
Benefits include:
- Consistency in naming and status
- Reliable document retrieval
- Reduced disputes
- Clear delivery milestones
Without a CDE, cloud adoption loses much of its strategic value.
How Cloud Platforms Redefine Team Collaboration

Perhaps the most transformative impact of cloud technology is how it changes human interaction within projects.
Collaboration shifts from delayed communication to continuous coordination.
Instead of waiting days for updates:
- Teams open shared models
- Review combined disciplines
- Comment directly in context
- Assign actions immediately
This environment allows professionals to:
- Work on federated models with live references
- Detect clashes earlier in the design process
- Raise RFIs linked to exact locations
- Attach photos, documents, and notes
- Allocate tasks to responsible parties
- Track resolution timelines
- Verify closures transparently
Meetings become more productive because participants rely on real-time information rather than static reports.
Owners and project managers gain visibility into progress without requesting manual updates.
The result is alignment across:
- Design
- Engineering
- Construction
- Procurement
- Operations planning
Everyone operates from the same digital foundation.
Real-Time Synchronization and Data Reliability
One of the most persistent problems in traditional project delivery is version uncertainty.
Teams frequently waste hours verifying whether they are working on the latest drawing, model, or specification.
Email exchanges, local downloads, and manual uploads make it difficult to establish a single source of truth.
Cloud environments solve this by connecting project participants to continuously updated information.
When data is modified within the system:
- Changes synchronize automatically
- Linked models refresh in near real time
- Sheets and schedules pull updated parameters
- Quantities reflect the latest design intent
- Dependencies remain aligned
Users no longer rely on verbal confirmations or separate file registers.
Modern platforms also support smart alert mechanisms.
Stakeholders receive notifications when:
- A model they depend on is updated
- A clash affects their scope
- A review is completed
- An approval status changes
Because everyone references the same live environment, trust in data improves dramatically.
Benefits include:
- Fewer coordination disputes
- Reduced rework
- Faster approvals
- Higher confidence during construction execution
Reliable information becomes a project asset rather than a recurring risk.
Information Transparency for Better Decisions
Senior leadership, project managers, and clients require visibility that goes beyond geometry.
They need measurable indicators of readiness, compliance, and risk exposure.
Cloud-connected ecosystems make this possible by converting project activity into structured, traceable metrics.
Decision-makers can monitor:
- Model development progress
- Discipline coordination performance
- Number and severity of clashes
- Outstanding RFIs
- Approval timelines
- Deliverable completeness
Instead of manually collecting reports from multiple teams, leaders access centralized dashboards built from live project data.
These tools help transform complex datasets into understandable intelligence.
With proper configuration, analytics can highlight:
- Bottlenecks delaying milestones
- Repeated coordination failures
- Areas with slow issue closure
- Potential cost or schedule impacts
This level of transparency supports proactive management rather than reactive troubleshooting.
For owners and consultants, it provides defensible documentation of how decisions were made.
Role of Cloud-Based BIM in Multi-Disciplinary Coordination

Today’s AEC projects rarely involve a single design team.
A typical development may include:
- Architects
- Structural engineers
- MEP designers
- Fire and life safety consultants
- Facade specialists
- Contractors and subcontractors
Without a shared environment, each discipline tends to operate in isolation, increasing the likelihood of conflicts.
Cloud workflows enable integration by allowing models from different authors to exist within one coordinated framework.
Teams can:
- Aggregate discipline models automatically
- Run clash detection routines
- Create shared viewpoints
- Apply controlled markups
- Record discussions directly against model elements
- Maintain centralized communication histories
Because interactions occur within the model context, misunderstandings decrease.
Participants see exactly where and why issues occur.
This approach improves:
- Meeting efficiency
- Responsibility assignment
- Resolution tracking
- Documentation reliability
Instead of fragmented conversations across emails and spreadsheets, collaboration becomes structured and searchable.
Lifecycle Benefits Beyond Design
The advantages of digital collaboration do not end once drawings are issued.
In fact, many organizations find the greatest value appears during construction and facility operations.
As projects move to execution, cloud-enabled information supports:
- Construction sequencing and planning
- Trade coordination
- Site logistics visualization
- Quantity validation
- Procurement alignment
Field teams can access updated data without waiting for office transmissions.
During handover, digital continuity ensures that asset information remains usable.
Owners and operators can leverage the model for:
- Equipment identification
- Warranty tracking
- Maintenance planning
- Space management
- Future renovations
Because historical decisions, approvals, and revisions are preserved, facilities teams inherit structured knowledge instead of disconnected files.
This long-term perspective is why many clients now mandate cloud participation from the earliest design stages.
Integration with Digital Construction Technologies

Modern cloud ecosystems rarely operate in isolation.
They function as connection hubs between design data, construction activities, and operational intelligence.
When models live in shared digital environments, they can feed other specialized systems automatically.
Common integrations include:
- 4D planning tools linking models to schedules
- 5D platforms connecting quantities with cost databases
- Digital twin frameworks reflecting real-time asset conditions
- IoT networks capturing performance and environmental data
- AR/VR solutions improving stakeholder visualization
- Predictive analytics identifying risks before they materialize
Instead of treating BIM as a static deliverable, cloud infrastructure turns it into a continuously evolving knowledge system.
Project teams gain the ability to simulate outcomes, test alternatives, and validate strategies before physical work begins.
This shift moves BIM from design support into strategic asset intelligence.
Security, Permissions, and Data Control

Moving information online naturally raises concerns about confidentiality and ownership.
Because of this, enterprise-grade cloud platforms are designed with multiple layers of protection.
Typical safeguards include:
- End-to-end encrypted communication
- Role-based access aligned with responsibility
- Multi-factor authentication for sensitive data
- Detailed user activity logs
- Automated backup and recovery systems
Administrators can define who can:
- View information
- Modify models
- Approve submissions
- Issue documentation
This structured governance prevents unauthorized actions while maintaining collaboration efficiency.
For regulated or high-value projects, audit trails also provide legal and contractual protection.
Challenges Organizations May Encounter
Despite clear advantages, adopting cloud workflows is not purely a technology decision.
It requires organizational alignment, cultural adaptation, and process maturity.
Common difficulties include:
- Resistance from teams comfortable with legacy methods
- Limited understanding of digital collaboration principles
- Complexity in transferring historical data
- Dependence on stable internet access
- Lack of standardized naming and approval structures
Without preparation, even the best technology may fail to deliver expected benefits.
Successful transitions usually involve:
- Clear leadership direction
- Defined workflow frameworks
- Gradual implementation strategies
- Continuous training and technical support
Digital transformation works best when people evolve along with the platform.
Comparing Cloud and Traditional BIM Approaches
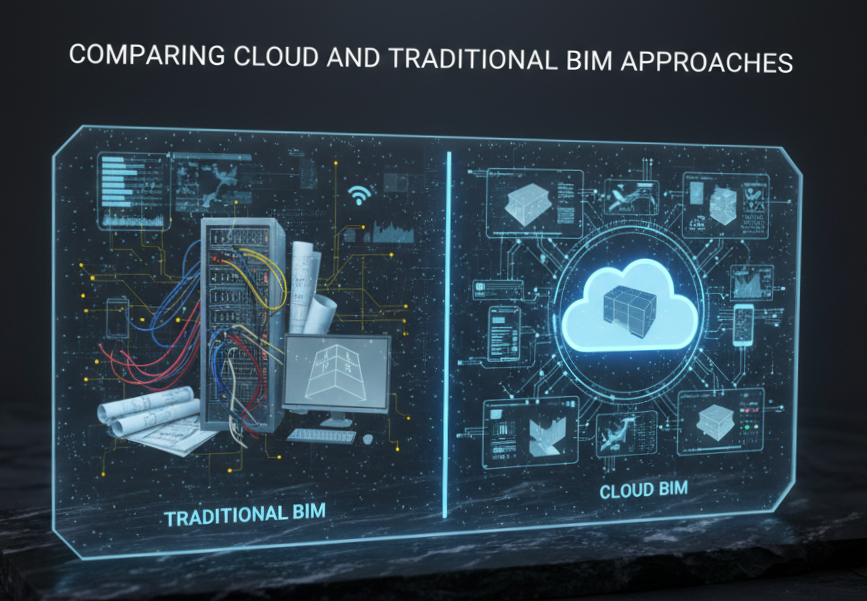
The contrast between methods explains why many organizations are rethinking their strategies.
Traditional Environments Often Rely On
- Email-based exchanges
- Local file storage
- Manual revision control
- Separate communication channels
- Heavy meeting dependency
These practices create fragmentation and increase the likelihood of errors.
Cloud-Enabled Environments Provide
- Centralized information repositories
- Automatic synchronization
- Transparent accountability
- Traceable decision histories
- Faster validation cycles
Instead of managing files, teams manage information.
The operational difference can significantly influence:
- Project profitability
- Delivery timelines
- Risk exposure
- Client satisfaction
Why Adoption Continues to Accelerate

Multiple global forces are pushing digital collaboration from innovation to necessity.
Key drivers include:
- International project partnerships
- Owners demanding real-time reporting
- Expanding regulatory frameworks
- Need for lifecycle-ready data
- Pressure to reduce disputes and claims
Many tenders now include explicit digital delivery requirements.
Organizations unable to demonstrate cloud capability may struggle to compete in advanced markets.
What was once optional is rapidly becoming a baseline expectation.
The Future Outlook
As infrastructure grows more complex, connected data environments will become even more intelligent.
Industry evolution is expected to move toward:
- Higher levels of workflow automation
- AI-assisted review and approval support
- Stronger cross-platform interoperability
- Embedded compliance verification
- Deeper integration with operational systems
Rather than isolated software packages, we are heading toward unified digital ecosystems.
The BIM model will act as a living reference throughout the entire asset lifecycle.
What This Means for Future Professionals
The industry will increasingly demand people who can:
- Work confidently inside cloud collaboration platforms
- Understand Common Data Environment structures
- Manage digital workflows across disciplines
- Interpret data for decision-making
- Support lifecycle information delivery
Simply knowing software commands will not be enough.
Build These Skills at BIM Cafe Learning Hub
At BIM Cafe Learning Hub, training is aligned with how the AEC industry is actually evolving.
Students and professionals learn:
- Practical cloud collaboration workflows
- Real coordination environments
- Industry documentation practices
- Project-based execution methods
- Skills that match international delivery standards
The goal is simple — move beyond theory and prepare you for the responsibilities modern BIM roles demand.
If you want to stay relevant in a future defined by connected construction and digital delivery, structured learning and real workflow exposure are essential.
Connect with BIM Cafe Learning Hub to understand how you can prepare for the next generation of BIM careers.
Conclusion
Cloud-Based BIM is fundamentally reshaping how the AEC industry creates, validates, and maintains information.
By enabling continuous collaboration, improving reliability, and supporting lifecycle intelligence, cloud environments establish a stronger foundation for predictable project delivery.
Organizations that embrace these workflows typically achieve:
- Better coordination
- Reduced rework
- Faster decisions
- Greater transparency
- Long-term operational value
Digital collaboration is no longer just a technical upgrade.
It is a strategic capability.