Author: Devika R
October 1, 2025
7 min read
Introduction
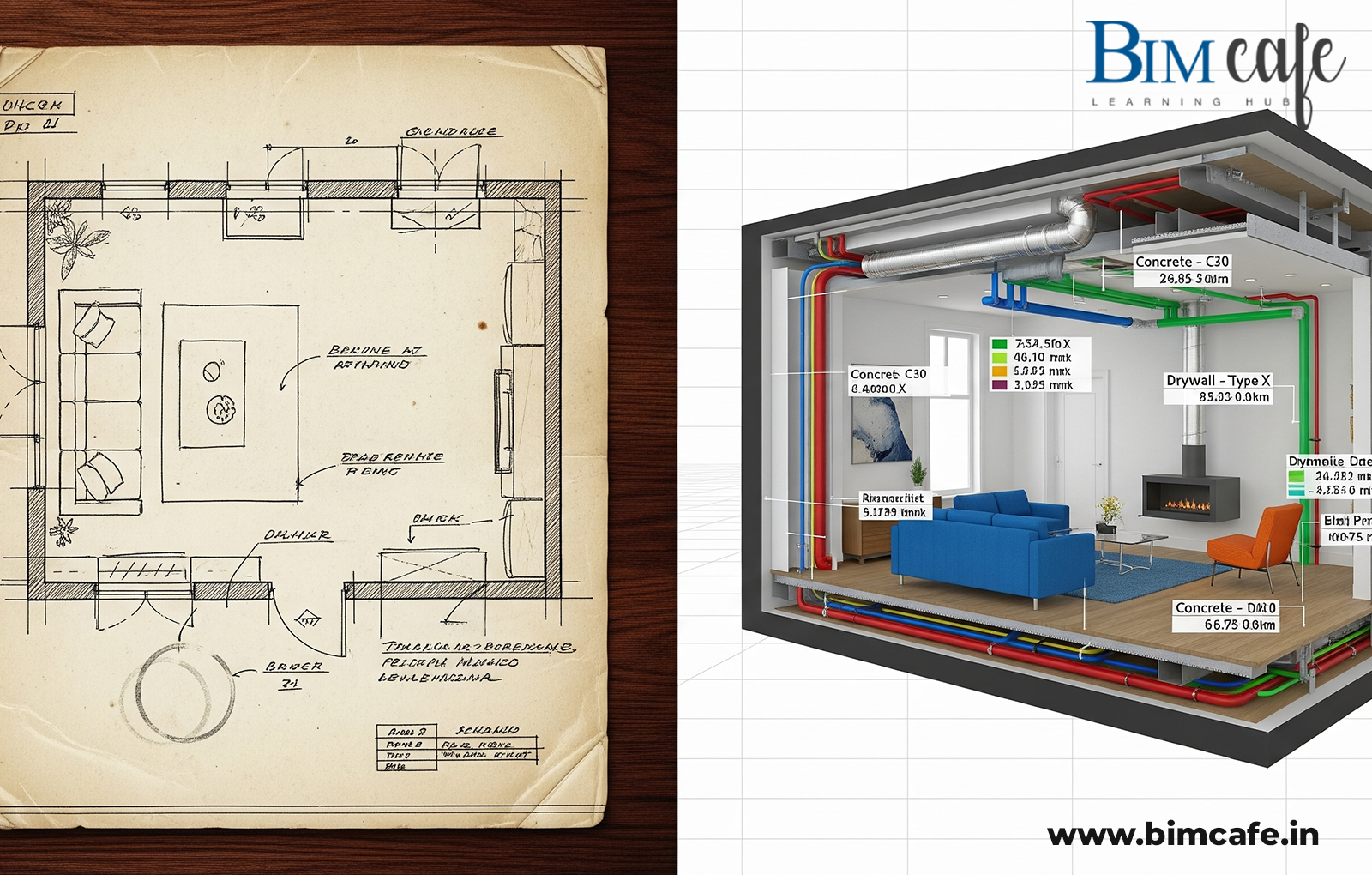
Interior design has always been about aesthetics, functionality, and creating spaces that resonate with people. But as client expectations rise and projects grow more complex, traditional 2D drawings and mood boards are no longer enough. Enter Building Information Modeling (BIM)—a technology that has redefined how buildings are designed and constructed, and now, how interiors are envisioned and delivered.
For interior designers, architects, and engineers, BIM offers more than 3D visuals. It brings coordination, cost transparency, material intelligence, and lifecycle management to the heart of interior projects. This blog explores how BIM is revolutionizing interior design and why future-ready professionals can’t afford to ignore it.
Why Traditional Interior Design Tools Fall Short

For decades, interior designers relied on:
- 2D drawings and sketches for layouts.
- 3D renders for visual appeal.
- Physical samples for material selection.
While effective, these methods often lacked accuracy, real-time collaboration, and integration with engineering systems. Common challenges included:
- Clash between design intent and structural/MEP layouts.
- Cost overruns due to inaccurate quantity take-offs.
- Delays when clients requested design revisions.
- Sustainability blind spots (material waste, inefficient lighting, HVAC).
BIM bridges these gaps by linking interior design with the broader AEC (Architecture, Engineering, Construction) ecosystem.
How BIM Transforms Interior Design
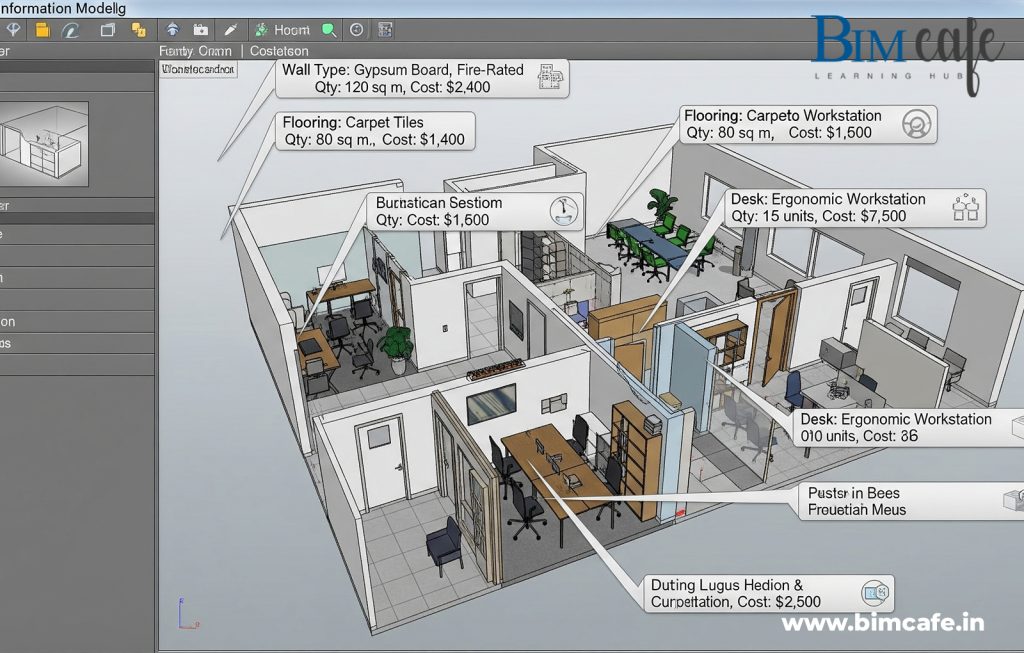
1. Smarter Space Planning
With BIM, interior designers can create highly detailed 3D models that are not just visual but also data-rich.
- Furniture layouts, lighting plans, finishes, and textures can be placed in models that also respect structural grids and MEP pathways.
- Designers can check real-time clearances, circulation paths, and ergonomics.
Example: A kitchen layout in BIM can instantly show whether cabinetry interferes with plumbing or electrical systems—something 2D drawings may miss.
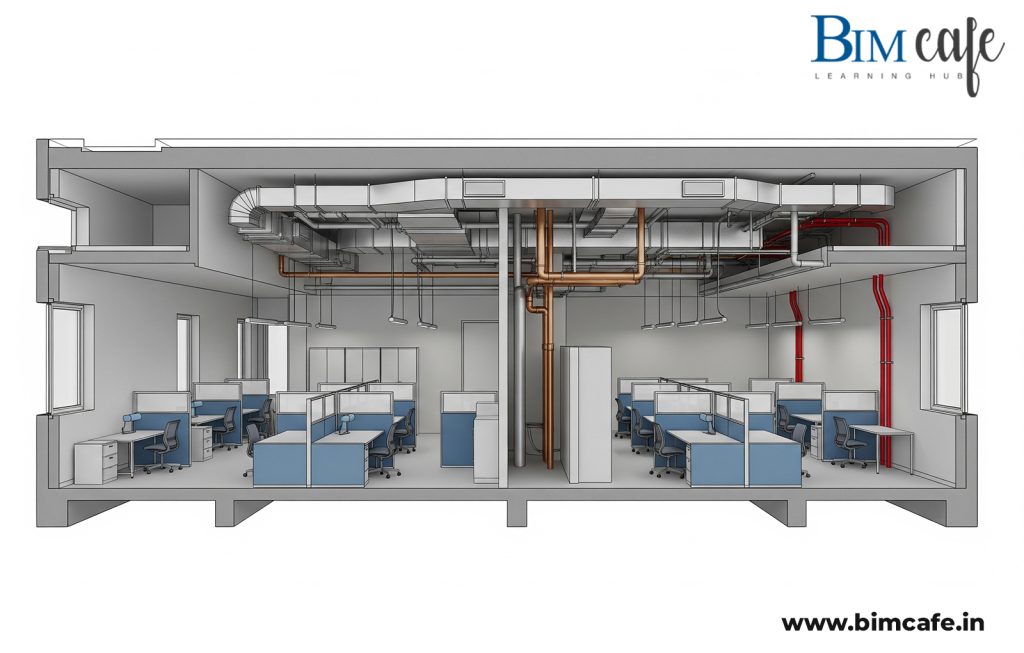
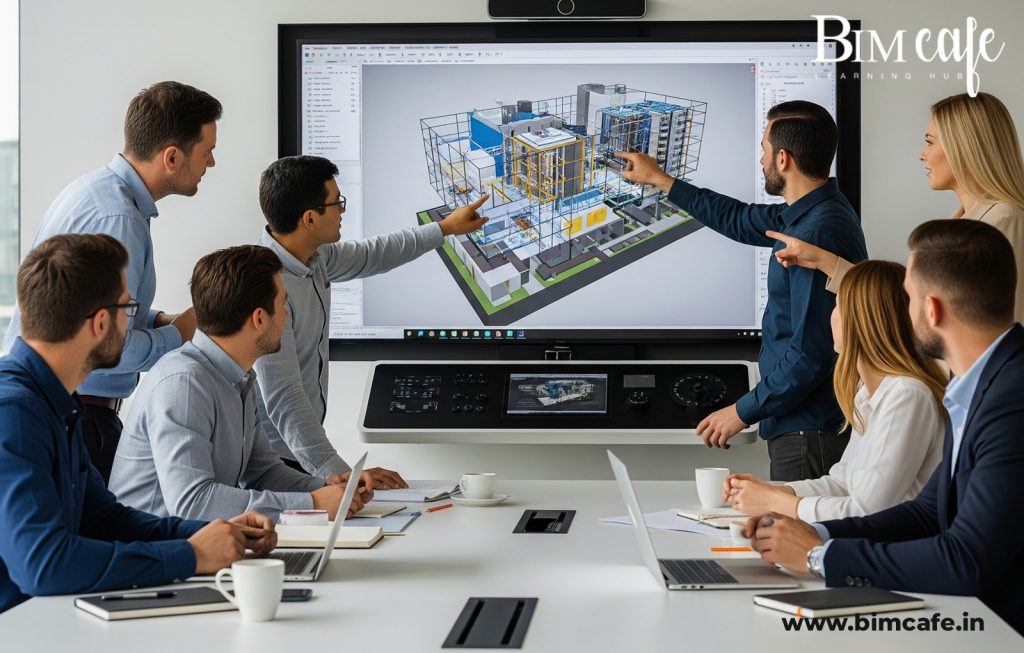
2. Seamless Coordination with Architects & Engineers
Interior design doesn’t exist in isolation—it must align with structural and MEP systems. BIM allows:
- Clash detection between false ceilings and ducting.
- Coordinated placement of electrical points for lighting and appliances.
- Integration of finishes without affecting load-bearing structures.
This multi-disciplinary approach reduces redesigns, delays, and costly errors during execution.
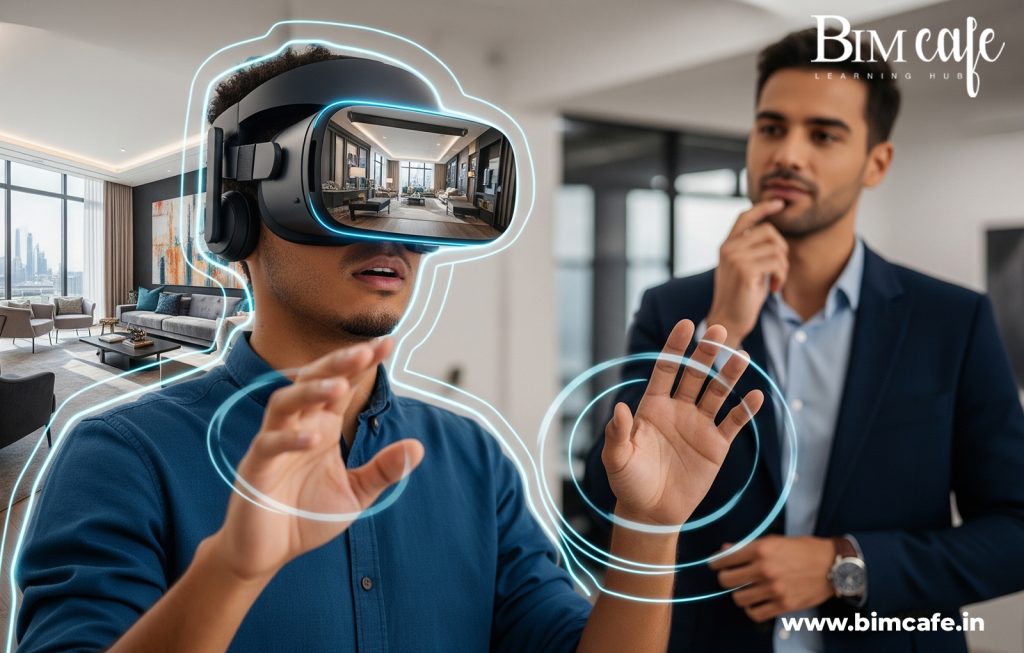
3. Visualization Beyond 3D
BIM enables immersive visualization tools that go far beyond traditional renders:
- Virtual Reality (VR) walk-throughs let clients experience spaces before they’re built.
- Augmented Reality (AR) overlays designs onto real sites for accurate previews.
- 360° BIM galleries provide interactive exploration of interiors.
These experiences boost client confidence, speed up approvals, and allow faster design iterations.
4. Cost & Material Intelligence
Every interior design decision has cost implications—BIM makes this transparent.
- Automated quantity take-offs provide accurate material requirements.
- Cost schedules update in real-time as design changes are made.
- Designers can compare finishes (e.g., wooden flooring vs. tile) not just visually, but also in terms of budget and sustainability.
This feature alone helps clients make informed decisions and prevents budget overruns.
5. Sustainability in Interiors
BIM integrates sustainability by:
- Simulating daylighting and energy use to optimize lighting and HVAC placement.
- Reducing material waste through precise cutting and prefabrication.
- Allowing lifecycle analysis of finishes (durability, maintenance).
Sustainable interiors are not just a trend—they’re becoming mandatory in global markets. BIM equips designers with the data to deliver eco-friendly projects.
6. Faster Revisions & Client Approvals
In traditional workflows, every design change meant redrawing, re-rendering, and re-quoting. With BIM:
- Designers can modify elements in the model, and changes auto-update across drawings, schedules, and cost sheets.
- Clients see instant updates in visualization, making decision-making quicker.
- Project timelines shorten significantly.
7. Facility Management & Post-Occupancy Benefits
BIM models don’t stop at design delivery—they extend into building operation. For interiors, this means:
- Facility managers can access data on finishes, furniture specs, and maintenance cycles.
- Asset tagging ensures easier replacement and repairs in the future.
- Digital twins can track wear-and-tear, ensuring longevity of interiors.
This lifecycle advantage sets BIM apart from traditional interior tools.
BIM vs Traditional Interior Design: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Interior Design | Interior Design with BIM |
| Drawings & Models | 2D drawings + static renders | Intelligent 3D + VR/AR visualization |
| Coordination | Manual, prone to errors | Automated clash detection with structure & MEP |
| Costing | Manual BOQ, prone to inaccuracy | Automated, real-time cost schedules |
| Sustainability | Limited, add-on analysis | Integrated energy/daylight/material simulations |
| Client Approvals | Slower, iterative | Faster, immersive experiences |
| Post-Occupancy | Minimal documentation | Facility management ready |
Why Interior Designers Need BIM Skills

The demand for BIM-trained interior designers is growing rapidly. Employers want professionals who can:
- Deliver accurate 3D models aligned with architects and engineers.
- Use tools like Revit, Navisworks, and BIM 360 for coordination.
- Generate precise BOQs and material schedules.
- Present immersive visualizations to clients.
For students and professionals, mastering BIM isn’t just about using software—it’s about staying relevant in a rapidly digitalizing industry.Why Interior Designers Need BIM Skills
The demand for BIM-trained interior designers is growing rapidly. Employers want professionals who can:
- Deliver accurate 3D models aligned with architects and engineers.
- Use tools like Revit, Navisworks, and BIM 360 for coordination.
- Generate precise BOQs and material schedules.
- Present immersive visualizations to clients.
For students and professionals, mastering BIM isn’t just about using software—it’s about staying relevant in a rapidly digitalizing industry.
Real-World Application
Example 1: Corporate Office Fit-Out
Using BIM, the design team coordinated ceiling panels with sprinkler systems and ducts, ensuring a seamless aesthetic without compromising safety. Cost overruns were cut by 20% due to precise material estimates.
Example 2: Residential Interiors
BIM enabled homeowners to virtually walk through their living room and kitchen, testing finishes before final approval. The immersive experience reduced change orders during construction.
Checklist: Integrating BIM into Interior Design Practice
For designers adopting BIM, here’s a practical roadmap:
✅ Learn BIM software tools (Revit for interiors, Navisworks for coordination).
✅ Understand levels of development (LOD) for interior elements (e.g., furniture at LOD 300-350).
✅ Collaborate with architects/MEP early in the process.
✅ Use BIM for material optimization and sustainability checks.
✅ Present designs with VR/AR for faster client approvals.
✅ Keep BIM models updated for facility management post-handover.
BIM has moved beyond structural and architectural design—it’s now transforming how interiors are conceived, visualized, and delivered. For interior designers, adopting BIM means smarter space planning, seamless coordination, faster approvals, accurate costing, and sustainable solutions.
At BIM Cafe Learning Hub, we train the next generation of designers and engineers to harness BIM not only as a modelling tool but as a collaborative, data-driven process that shapes the interiors of tomorrow.