Author: Devika R
November 24, 2023
3 min read
In the modern era, as the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and sustainable development, the importance of energy-efficient building design cannot be overstated. Buildings account for a significant portion of global energy consumption, and optimizing their energy efficiency is crucial for reducing environmental impact and lowering operational costs. One powerful tool that architects and engineers use to achieve this goal is Autodesk Revit MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing), a Building Information Modeling (BIM) software that facilitates integrated and collaborative design processes. In this article, we will explore how Revit MEP can be leveraged to optimize energy efficiency in building designs.
BIM for Integrated Design

Revit MEP operates on the principles of Building Information Modeling, enabling architects, engineers, and other stakeholders to collaborate seamlessly throughout the design process. BIM allows for the creation of a digital representation of the building, encompassing its geometry, spatial relationships, geographic information, and other relevant data. This integrated approach fosters better communication among design disciplines and helps identify opportunities for energy efficiency improvements early in the design phase.
Performance Analysis and Simulation
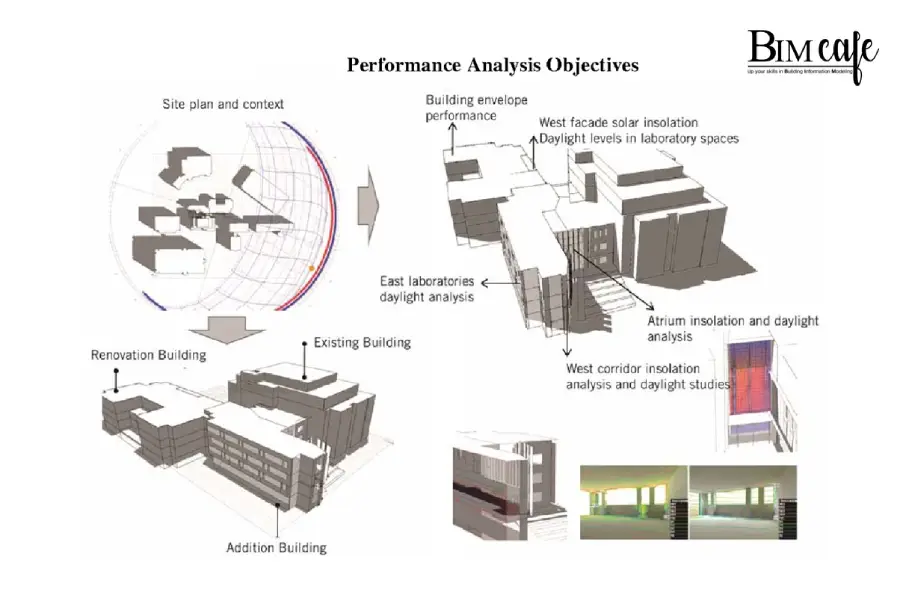
Revit MEP offers advanced simulation and analysis tools that enable designers to evaluate the performance of building systems and components. Energy analysis tools within the software allow users to simulate and analyze the energy consumption of the building, identifying areas for improvement. By evaluating different design scenarios, architects and engineers can make informed decisions to optimize energy efficiency while considering factors such as daylighting, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems, and insulation.
Sustainable HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems play a significant role in a building’s energy consumption. Revit MEP allows designers to model and simulate HVAC systems, helping to optimize their efficiency. By analyzing factors such as airflows, thermal loads, and equipment specifications, designers can identify opportunities to enhance HVAC system performance. Additionally, the software facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and geothermal systems, into the overall building design.
Lighting Design and Daylighting Analysis
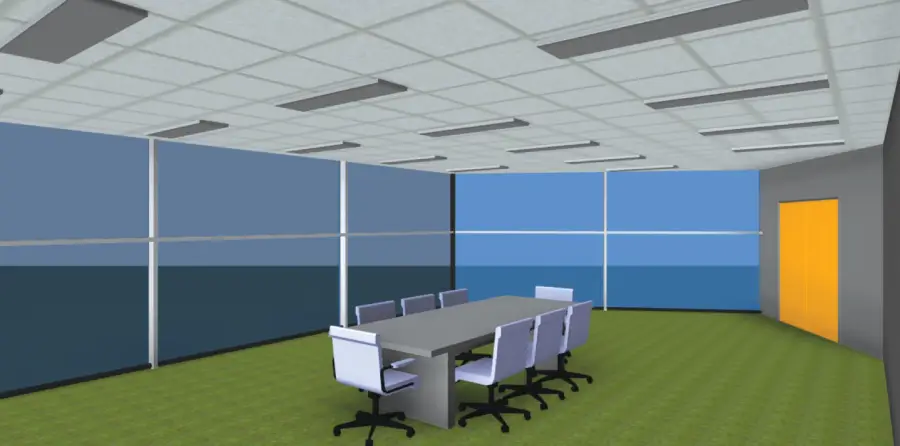

Proper lighting design is essential for both occupant comfort and energy efficiency. Revit MEP enables designers to model and simulate lighting systems, taking into account factors such as natural daylight. Daylighting analysis tools help determine the optimal placement of windows and skylights to maximize natural light while minimizing the need for artificial lighting. This not only reduces energy consumption but also enhances the overall quality of the indoor environment.
Parametric Design for Optimization
Revit MEP’s parametric design capabilities allow designers to create intelligent, adaptable building components. By establishing parameters for various design elements, such as insulation levels, window types, or HVAC system specifications, designers can quickly test and iterate different design scenarios. This iterative process empowers designers to identify the most energy-efficient solutions for a given set of conditions, leading to more sustainable building designs.
Compliance with Energy Codes and Standards

Revit MEP provides tools that assist designers in ensuring compliance with energy codes and standards. By incorporating these regulations into the digital model, designers can track and validate the building’s performance against specific energy efficiency criteria. This not only helps meet regulatory requirements but also ensures that the building operates efficiently throughout its lifecycle.